We explain what a plateau is, how it forms, and discuss its types and characteristics. In addition, we explore the largest and highest plateaus in the world.
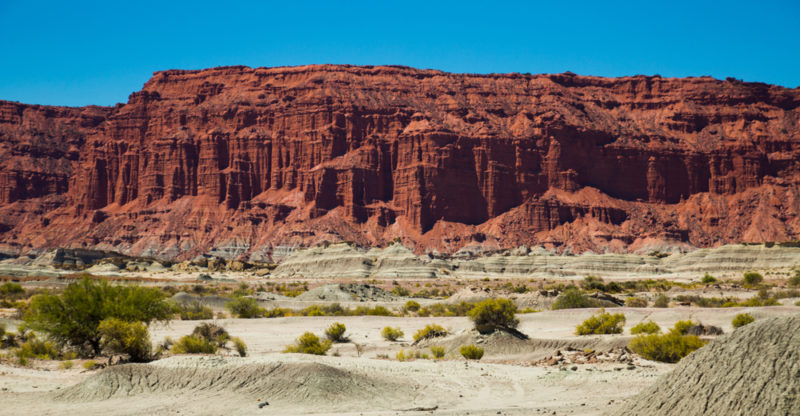

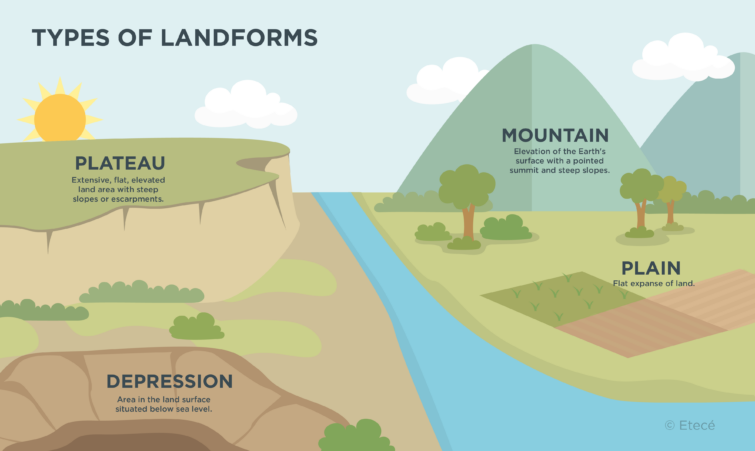
What is a plateau?
A plateau is an elevated flat-surfaced area that rises above the surrounding land. The elevation of plateaus may range from a few hundred feet to the Tibetan Plateau, which at over 14,800 feet (4,500 m) of average elevation, is the highest in the world.
The formation of plateaus mainly occurs due to tectonic uplift. This means that tectonic plate movement sometimes causes large expanses of land to rise above the surrounding terrain. Plateaus can also form as a result of erosion and volcanic activity.
In addition to continental plateaus, submarine or oceanic plateaus exist, which are flat-surfaced elevations formed on the seafloor. Underwater plateaus are extensions of the Earth's crust rising above the ocean floor. Their formation is linked to volcanic activity occurring on the seabed.
- See also: Physical geography of the Americas
How are plateaus formed?
Plateaus form as a result of geological processes acting on the Earth's crust over long spans of time. Key factors to the formation of plateaus are:
- Tectonic processes. The movement of tectonic plates may cause uplifts in the Earth's crust. In particular, when a plate collides with and pushes against another, it may cause large expanses of land to raise and flat areas to form that stand at a higher elevation than the surrounding lands.
- Volcanic processes. The volcanic origin of plateaus is related to the accumulation of materials from the planet's interior, which cool and solidify. Through successive eruptions, volcanic activity contributes to the formation of elevated tablelands made up of solidified lava.
- Erosional processes. Over geologic time, erosion gradually wears away the surface layers of Earth's outer crust. The constant action of agents of erosion such as wind and water erodes certain crustal materials while leaving more resistant ones raised.
Oceanic plateaus
Oceanic plateaus are flat, elevated landforms found on the seafloor. They form as a result of underwater tectonic and volcanic activity. Seafloor spreading, caused by activity at mid-ocean ridges, can lead to the formation of submarine plateaus, as tectonic plates drift apart.
Likewise, underwater volcanic eruptions also contribute to the uplift of submarine plateaus by accumulating molten lava that solidifies upon contact with ocean water.
One of the world’s major submarine plateaus is found in Oceania. Its name is Ontong Java Plateau, and is located in the Pacific Ocean, north of Australia. It covers an area of 580,000 square miles (1.5 million km2) and lies at about 6,565 feet (2,000 m) deep.
Buttes and chapadas
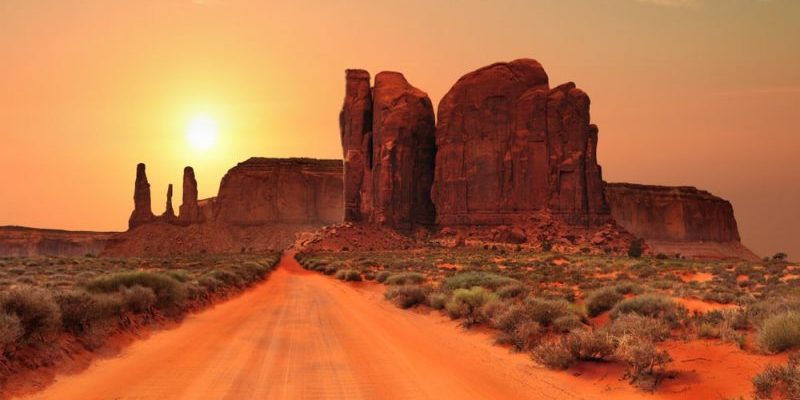

A butte is a small flat-topped plateau with steep cliffs on all sides. These formations are the result of erosional processes acting on layers of rock with varying levels of resistance. This means that more resistant materials form the flat top of the butte, while erosion wears away softer materials, creating the characteristic cliffs of these landforms.
A chapada is also a raised plateau or high plain bordered by cliffs or escarpments. However, it differs from a butte in its geological origin, since the formation of chapadas is usually the result of tectonic processes. Thus, layers of resistant rocks are uplifted due to tectonic activity. As is the case with buttes, erosion subsequently removes softer materials, forming cliffs.
Major plateaus on Earth
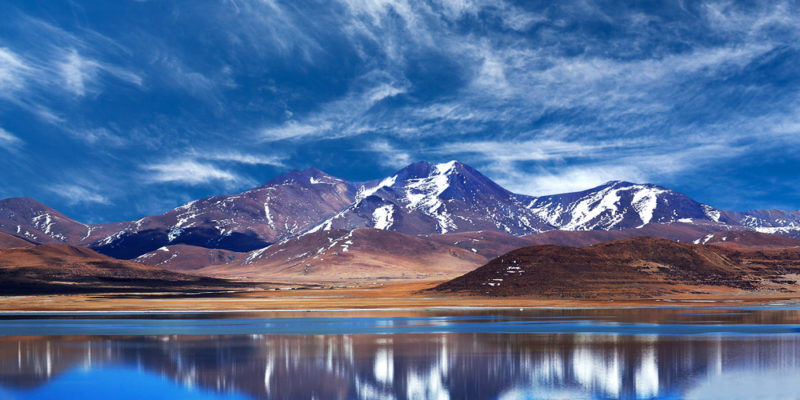

Some of the most important plateaus in the world are:
- Tibetan Plateau. Situated in Central Asia, the Tibetan Plateau is the largest and highest plateau in the world. With an average elevation of about 14,800 feet (4,500 m) above sea level, it spans areas of China, India, Nepal, and Bhutan. It is surrounded by the Himalayan, Kunlun, and Karakoram mountain ranges.
- Altiplano. Located in South America, the Altiplano covers part of Bolivia, Peru, Chile, and Argentina. It has an average elevation of about 12,300 feet (3,750 m) above sea level, and is surrounded by the Andes mountain chain.
- Deccan Plateau. Situated in central India, the Deccan Plateau is surrounded by the Vindhya Mountains to the north, and the Western and Eastern Ghats to the west and east respectively. It has an average elevation of about 1,805 feet (550 m) above sea level.
Explore next:
References
- Decología.info. (s.f.). Meseta. Definición, tipos, proceso formativo e importancia. https://decologia.info/
- Embajada de la República Popular China en la República Oriental del Uruguay. (2017). Geografía de Tíbet. http://uy.china-embassy.gov.cn/
- Tarbuck, E. y Lutgens, F. (2005). Ciencias de la Tierra. Una introducción a la geología física. Pearson Educación.



Was this information useful to you?
Yes NoThank you for visiting us :)