We explain what geology is, and discuss its field of study and branches. In addition, we explore its characteristics, uses, and more.

What is geology?
Geology is the science that studies the composition and evolution of planet Earth. Scientists who work in this discipline are called geologists.
The study of geology is divided into two main branches: physical geology and historical geology. Physical geology is concerned with the composition of the Earth and seeks to account for the various processes that occur on and beneath the planet's surface. Historical geology, in turn, aims to understand the origin of the Earth and its evolution over geologic time.
The main method of geology is field observation and the analysis of the processes occurring on the surface and interior of the Earth. Part of the research takes place in laboratories, where earth materials are analyzed.
Geology makes use of other disciplines, which contribute their methods and knowledge to the study of the Earth. Among the most important are physics, chemistry, and biology.
The term geology is composed of two parts: geo, meaning Earth, and logos, meaning reason or study, i.e., it is the study of the Earth. There is much debate as to who was the first scientist to coin the term. While some argue it was the Italian naturalist Ulisse Aldrovandi, others hold it was Swiss geologist and meteorologist Jean André Deluc. Other scholars, in turn, claim it was Swiss geologist Horace-Bénédict de Saussure, while for others it was German physician Abraham Gottlob Werner.
- Ver además: Precambrian
Characteristics of geology
Among the main characteristics of geology are:
- It studies the composition and geological history of the Earth.
- It is divided into two main branches: physical geology and historical geology.
- It divides the history of planet Earth into major periods called geological eras.
- It is a major discipline from which many other sciences derive, including paleontology, stratigraphy, and mineralogy.
- It draws from disciplines such as biology, physics, and chemistry.
- It provides knowledge that helps identify and prevent seismic and volcanic hazards.
History of geology
Questions concerning the origin, history, and composition of the Earth have been raised by humans for thousands of years. Before the emergence of geology as a science, philosophers, mathematicians, and religious figures tried to address these questions.
During the 17th and 18th centuries, the doctrine of catastrophism spread in Europe. Catastrophists believed that the Earth's landscape features had been created by great, sudden catastrophes. It was not until the late 17th and early 18th centuries that geology was established as a modern science.
James Hutton was a Scottish physician who published Theory of the Earth, a late 17th-century work considered to have laid the foundations for geology. In it, he argues that the physical, chemical, and biological laws at work today are the same as they were in the past. Furthermore, he seeks to demonstrate that the Earth's formation times are extremely slow and must be measured on a different scale from that of human time.
While Hutton and other scientists of the time were able to establish that geologic time was extremely long, they lacked the necessary methods to accurately determine the age of the Earth. It was not until the 19th century, with relative dating methods, that it was possible to begin to determine the age and major geological events in the history of the Earth.
Relative dating methods are techniques that help define the order in which geological events occurred. They are useful for understanding the sequence of events in history without the need to establish exact dates.
What does geology study?
Geology has two main branches of knowledge: physical geology and historical geology.
- Physical geology. It is concerned with the processes and composition of the Earth. It aims to understand how geological processes work and how they interact with the various components of the planet. Among the aspects it covers are mineralogy (the study of minerals), petrology (the study of rocks), geomorphology (the study of the shape and structure of the Earth's surface), and seismology (the study of earthquakes).
- Historical geology. It is concerned with the evolution of the Earth over geologic time. Through the analysis of rock strata and fossils, it seeks to reconstruct the history of the planet and explain how it has changed over millions of years. Among the aspects it covers are stratigraphy (the study of rock layers and their formation), paleontology (the study of fossils), chronostratigraphy (the study of the subdivision and correlation of geologic time), and paleoclimatology (the study of climate throughout Earth's history).
Branches of geology

Like all sciences, geology encompasses an important number of branches or sub disciplines that focus on specific aspects of geological knowledge. Among the most important are:
- Mineralogy. It is concerned with the study of minerals formed during the geological history of Earth.
- Petrology. It is concerned with the formation of the various types of rocks.
- Sedimentology. It studies the deposits of organic matter and other forms of sediment over the geological periods.
- Paleontology. It deals with the study of fossils to account for life forms over Earth's geological past.
- Structural geology. It studies how the rocks and layers of the Earth are structured, arranged, and deformed. It is central to the study of seismic hazards.
- Economic geology. It is concerned with the study of mineral resources from a commercial perspective. It centers on the exploration, identification, location, and extraction of mineral resources.
- Geochemistry. It deals with the chemical composition of the elements that make up the interior and surface of the Earth.
How is geology related to other sciences?

Given its interdisciplinary nature, geology relates to multiple sciences that contribute their knowledge to the understanding of the Earth. Some of these are:
- Biology. Paleontology, a branch of geology, is related to biology through the study of fossils and the evolution of living beings over geologic time. In addition, geological changes may affect habitat formation and the interaction between living beings and their geological environment.
- Chemistry. Geology makes use of chemical principles to understand the composition of the Earth and the chemical processes that occur inside it.
- Physics. Geology relies on laws of physics to study processes and phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and magnetic fields. Seismology, for example, is based on the physics of seismic waves.
- Mathematics. Geology uses mathematical tools to model and analyze geologic data, interpret seismic and geodetic data, and calculate rates of erosion, degradation, and other geologic processes.
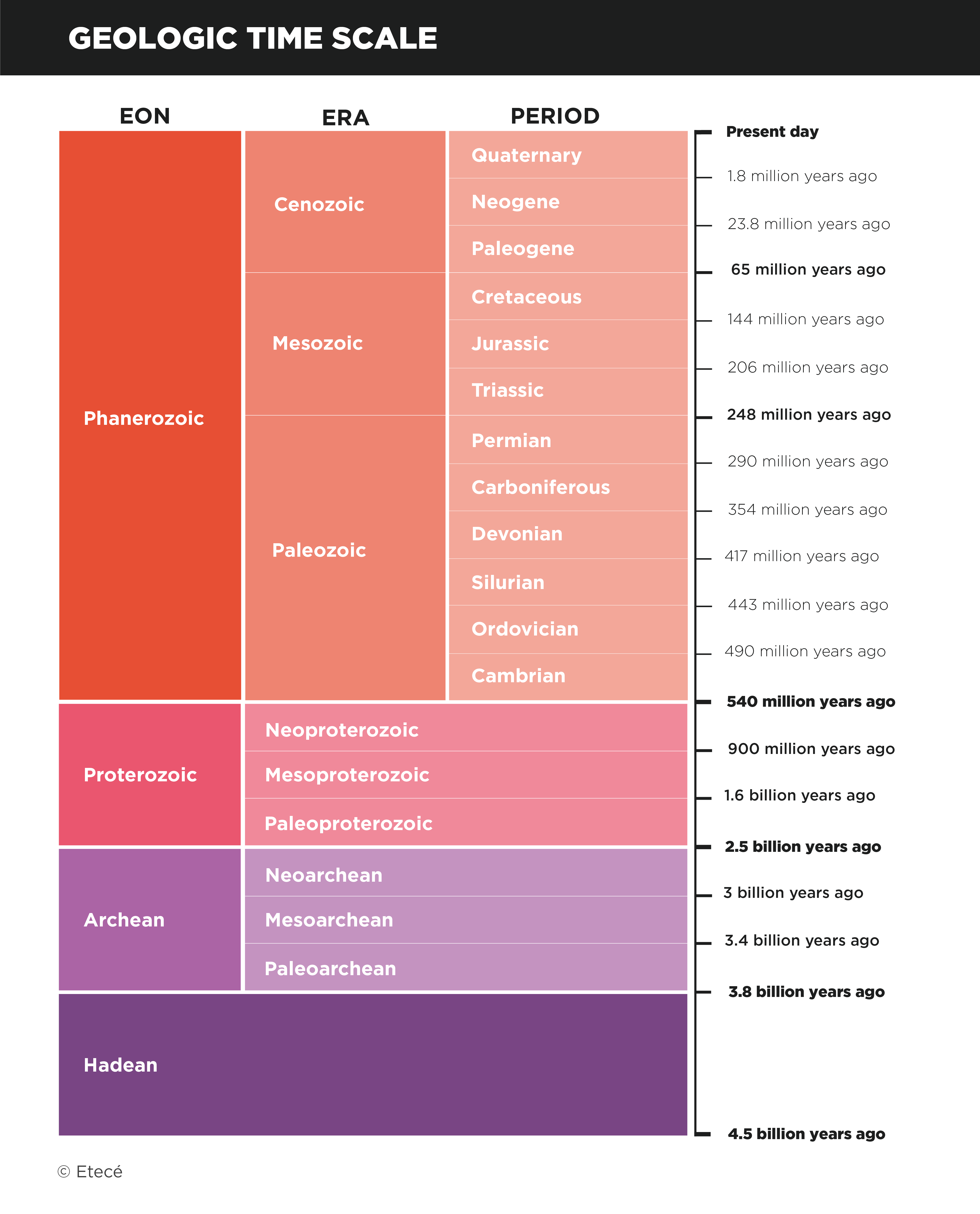
Geologic time
Geologic time makes reference to the history of Earth's formation, from its origin to the present day. The geologic time scale divides geologic time into large spans of time called geological eras. Geological eras cover periods of time that are extremely long compared to human time.
There are nine geological eras, over which Earth’s formation and transformation took place, as well as the emergence of life on the planet, its complexification, and diversification. The geological eras are:
- Paleoarchean
- Mesoarchean
- Neoarchean
- Paleoproterozoic
- Mesoproterozoic
- Neoproterozoic
- Paleozoic
- Mesozoic
- Cenozoic
What does a geologist do?

Mining and oil and gas industries, as well as hydroelectric and civil engineering projects (including the construction of highways and tunnels) involve the work of geologists. Knowledge of the dynamics of the Earth's interior is key in projects that entail drilling and work beneath Earth’s surface.
In addition, the work of geologists is of great importance for warning and preventing geologic hazards. Their skills are highly sought after in organizations and companies dedicated to the prevention of earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.
Furthermore, geology provides valuable information to astronomy, since the study of the Earth's composition allows for formulating hypotheses regarding the composition of other planets.
Explore next:
References
- Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Museo (Universidad Nacional de La Plata). (s.f.). Licenciatura en Geología. https://www.fcnym.unlp.edu.ar/
- Indeed. (2023). Conoce las ramas de la geología. https://www.indeed.com/
- Tarbuck, E. y Lutgens, F. (2005). Ciencias de la Tierra. Una introducción a la geología física. Pearson Educación.
Was this information useful to you?
Yes NoThank you for visiting us :)